Face recognition technology has emerged as one of the most impactful advancements in the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning. It’s widely used in various applications, from security systems and smartphone authentication to social media tagging and retail analytics. Consequently, understanding how face recognition algorithm function is crucial for those interested in leveraging this technology. Therefore, this comprehensive guide explores the fundamentals of face recognition algorithms, their types, working principles, practical applications, and ethical considerations. By delving into these aspects, you can gain a thorough understanding of face recognition systems.
Fundamentals of Face Recognition Algorithms
Before diving into the complexities of face recognition algorithm, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals. These basics lay the groundwork for grasping more advanced concepts. Therefore, exploring the fundamentals of face recognition algorithms is crucial.
What is Face Recognition?
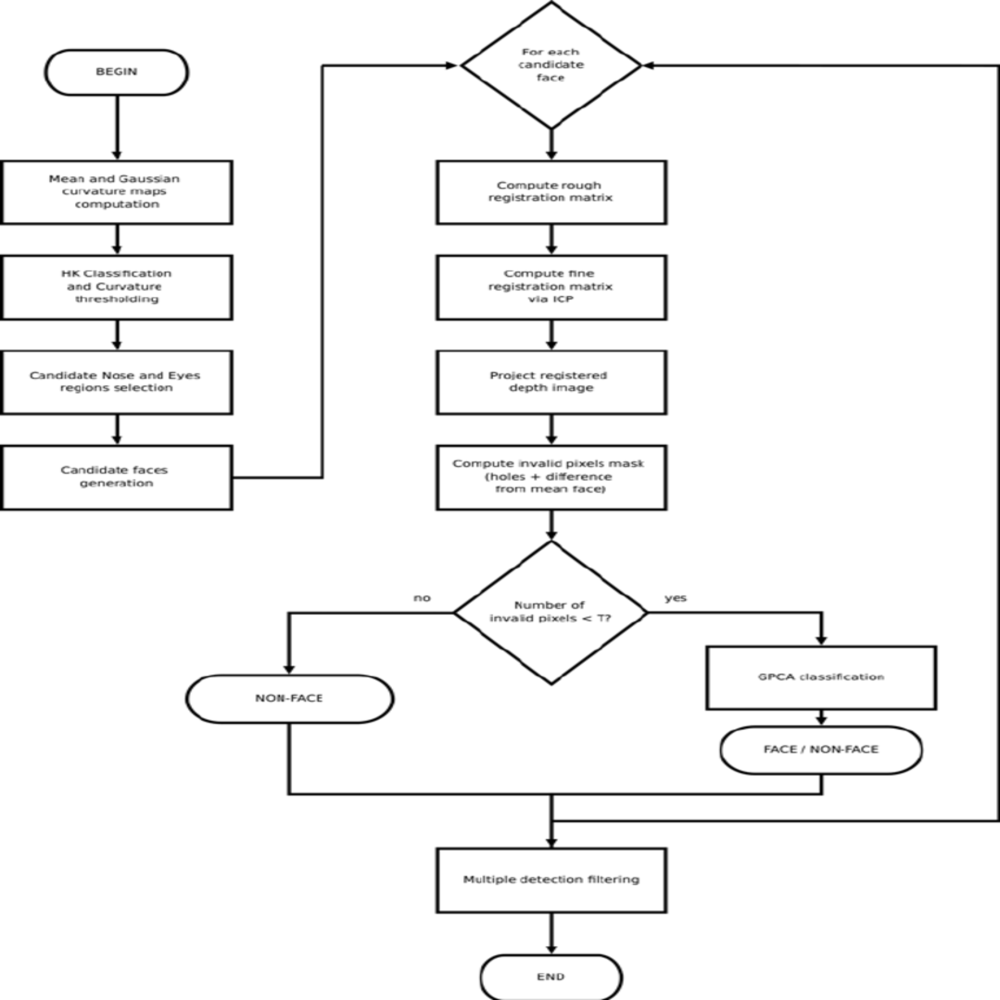
Face recognition involves identifying or verifying a person’s identity using their facial features. This process typically consists of three main tasks: detection, alignment, and recognition. Detection involves locating faces within an image or video frame. Alignment ensures all detected faces are oriented similarly for further processing. Recognition either compares the aligned face to a database of known faces for identification or verifies the face against a claimed identity. By understanding the core components of face recognition, you can appreciate its complexity and capabilities. Therefore, recognizing the necessity of these tasks is crucial.
Evolution and History
Face recognition algorithms have evolved significantly since their inception. Early methods relied on simple geometric models, measuring distances between facial landmarks like the eyes, nose, and mouth. However, these methods had limited accuracy and robustness. The advent of machine learning and deep learning revolutionized the field by introducing more sophisticated techniques, such as eigenfaces and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). These advancements drastically improved the accuracy and reliability of face recognition systems. By understanding the evolution and history of face recognition algorithms, you can appreciate how far the technology has come. Therefore, recognizing the advancements in the field is essential.
Types of Face Recognition Algorithms
Several types of face recognition algorithms exist, each leveraging different techniques and methodologies. Understanding these types helps in selecting the most appropriate algorithm for specific applications. Therefore, exploring the various types of face recognition algorithms is essential.
Geometric-Based Algorithms
Geometric-based algorithms are among the earliest methods used for face recognition. These algorithms analyze the geometric relationships between facial landmarks, such as the distance between the eyes or the shape of the chin. Techniques like the Fisherface and Eigenface algorithms fall under this category. Although simple in approach, geometric-based algorithms have limited accuracy and are sensitive to variations in lighting, pose, and facial expressions. By understanding geometric-based algorithms, you can see their foundational role in the field. Therefore, recognizing their limitations is crucial.
Feature-Based Algorithms
Feature-based algorithms focus on extracting distinct facial features and using them for identification or verification. Local Binary Patterns (LBP), Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT), and Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) are examples of feature-based methods. These algorithms analyze texture, edges, and other specific traits of the face, making them more robust to changes in lighting and pose than geometric-based methods. However, they still struggle with significant variations in facial expressions. By understanding feature-based algorithms, you can see their enhanced capabilities. Therefore, recognizing their strengths and weaknesses is essential.
Deep Learning-Based Algorithms
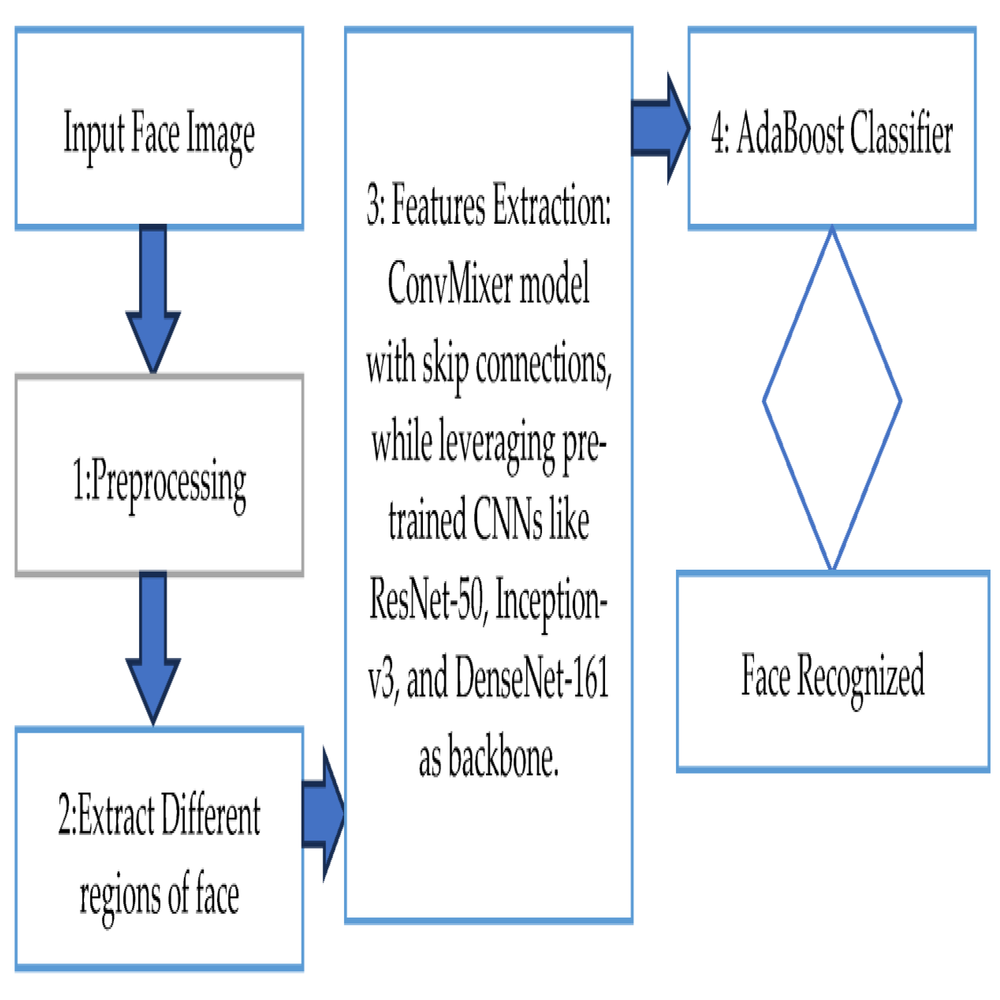
Deep learning-based algorithms represent the latest and most advanced approach to face recognition. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and their variants, such as ResNet and VGGNet, are extensively used in deep learning models for face recognition. These algorithms automatically learn to extract features from images, significantly improving accuracy and robustness. Techniques like FaceNet and DeepFace leverage large datasets and deep learning architectures to achieve state-of-the-art performance. By understanding deep learning-based algorithms, you can appreciate their transformative impact on face recognition. Therefore, recognizing their superiority is crucial.
Working Principles of Face Recognition Algorithms
Understanding the working principles behind face recognition algorithms illuminates how these systems operate and achieve high accuracy. Therefore, exploring the working principles is essential.
Face Detection and Alignment
The face detection phase involves locating faces within an image or video frame. Techniques like Haar Cascades, YOLO (You Only Look Once), and Multi-Task Cascaded Convolutional Networks (MTCNN) are commonly used for this purpose. Once detected, face alignment ensures that all faces are oriented consistently, accounting for variations in pose, scale, and rotation. Algorithms like Affine transformations and facial landmark detection methods are employed to achieve precise alignment. By understanding the importance of detection and alignment, you can appreciate the foundation of face recognition. Therefore, recognizing these initial steps is crucial.

Feature Extraction
Feature extraction is a critical step where the unique characteristics of each face are identified. For geometric-based and feature-based algorithms, this involves measuring distances between landmarks or analyzing texture and edges. In deep learning-based algorithms, convolutional layers automatically learn to extract hierarchical features from raw pixel data. Techniques such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), and deep neural networks are employed to distill these features. By understanding the feature extraction process, you can see how algorithms distinguish between different faces. Therefore, recognizing its significance is essential.
Face Matching and Recognition
The final step is face matching and recognition, where the extracted features are compared to a database of known faces. In identification scenarios, the algorithm matches the face against all entries in the database to find the closest match. In verification tasks, it compares the face to a claimed identity to confirm or deny the match. Techniques like cosine similarity, Euclidean distance, and Support Vector Machines (SVM) are used for comparison and classification. By understanding the matching and recognition process, you can appreciate how face recognition algorithms achieve reliable results. Therefore, recognizing these concluding steps is crucial.
Practical Applications of Face Recognition Algorithms
Face recognition algorithms have a wide range of practical applications across various industries. Understanding these applications showcases the versatility and impact of this technology. Therefore, exploring practical applications is essential.
Security and Surveillance
One of the most prominent applications of face recognition technology is in security and surveillance. Airports, casinos, and other high-security environments use face recognition systems to monitor and identify individuals in real-time. These systems can detect known criminals or persons of interest, enhancing public safety and security. Law enforcement agencies also leverage face recognition for identifying suspects in criminal investigations. By understanding the role of face recognition in security, you can appreciate its significant contributions to public safety. Therefore, recognizing its impact on security is crucial.
Access Control and Authentication
Face recognition is increasingly used for access control and authentication in various settings. Biometric authentication systems employ face recognition to grant access to secure areas, devices, and systems. For example, smartphones and laptops use face recognition for unlocking and verifying user identity. This technology offers a convenient and secure alternative to traditional passwords and PINs. By understanding the applications of face recognition in access control, you can see its potential to enhance security and convenience. Therefore, recognizing its value in authentication is essential.
Retail and Marketing
In the retail sector, face recognition technology provides valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences. Retailers use face recognition to track foot traffic, analyze customer demographics, and measure engagement with products. This data enables personalized marketing and advertising strategies, improving customer experience and boosting sales. Loyalty programs also employ face recognition to enhance customer interactions and streamline rewards processing. By understanding the applications of face recognition in retail, you can appreciate its impact on marketing and customer engagement. Therefore, recognizing its benefits for retailers is crucial.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
The widespread adoption of face recognition technology raises ethical considerations and challenges that must be addressed. Understanding these issues helps balance technological advancement with societal values. Therefore, exploring ethical considerations and challenges is essential.
Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns are among the most significant ethical issues associated with face recognition technology. The ability to identify and track individuals in real-time raises questions about consent and data ownership. Unauthorized use of face recognition can lead to violations of personal privacy and civil liberties. Implementing robust privacy policies and ensuring transparency in data collection and usage are essential steps to address these concerns. By understanding the privacy implications, you can advocate for responsible use of face recognition technology. Therefore, recognizing the importance of privacy is crucial.
Bias and Fairness
Bias and fairness are critical challenges in the development and deployment of face recognition algorithms. Studies have shown that some algorithms exhibit biases, performing less accurately on certain demographic groups, such as people of color or women. These biases can result in unfair treatment and discrimination. Ensuring diversity in training datasets and rigorously testing algorithms for biases are essential steps to mitigate these issues. By understanding the importance of fairness, you can advocate for more ethical and unbiased face recognition systems. Therefore, recognizing the significance of addressing bias is crucial.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
The rapid adoption of face recognition technology necessitates the development of legal and regulatory frameworks to govern its use. Regulations should address issues such as data protection, consent, and accountability. Legislators and policymakers must work together to create laws that balance the benefits of face recognition with the protection of individual rights. By understanding the need for legal and regulatory frameworks, you can support the development of responsible and ethical guidelines. Therefore, recognizing the importance of regulation is essential.
Addressing Common Questions About Face Recognition Algorithms
Understanding common questions about face recognition algorithms provides additional clarity and guidance. Knowledge of these answers ensures better preparation and confidence. Therefore, exploring common questions is essential.
How Accurate Are Face Recognition Algorithms?
A common question concerns the accuracy of face recognition algorithms. The accuracy of face recognition algorithms depends on several factors, including the quality of the training data, the algorithm used, and environmental conditions. State-of-the-art algorithms like FaceNet and DeepFace achieve high accuracy rates, often exceeding 99%. However, performance can vary depending on lighting, angle, and occlusions. By understanding the factors influencing accuracy, you can appreciate the capabilities and limitations of face recognition algorithms. Therefore, recognizing the importance of these factors is crucial.
Can Face Recognition Be Fooled?
Another common question is whether face recognition systems can be fooled. While advanced algorithms are highly robust, face recognition systems can still be vulnerable to spoofing attacks, such as using photographs, masks, or deepfake videos. Techniques like liveness detection, which monitors blinking or 3D facial contours, help mitigate these risks. By understanding the vulnerabilities and protective measures, you can appreciate the complexity of securing face recognition systems. Therefore, recognizing the importance of anti-spoofing techniques is essential.
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Face Recognition Algorithms
Addressing common misconceptions about face recognition algorithms provides accurate information and dispels concerns. Clarifying misunderstandings ensures an informed perspective. Therefore, this section explores common misconceptions about face recognition algorithms.
Misconception: Face Recognition Is 100% Accurate
A common misconception is that face recognition algorithms are 100% accurate. While advanced algorithms achieve high accuracy rates, no technology is infallible. Factors such as lighting, angle, and occlusions can affect performance. Continuous improvements in algorithms and training data help enhance accuracy, but occasional errors are inevitable. By understanding the limitations of face recognition algorithms, you can manage expectations and advocate for continued advancements. Therefore, dispelling this misconception emphasizes the need for ongoing development.
Misconception: Face Recognition Eliminates Privacy
Another misconception is that face recognition technology inherently eliminates privacy. While the potential for privacy invasion exists, responsible use and stringent regulations can address these concerns. Implementing policies that prioritize transparency, consent, and data protection can balance technological benefits with individual privacy rights. By understanding the measures to protect privacy, you can advocate for ethical face recognition practices. Therefore, dispelling this misconception highlights the importance of privacy measures.
Conclusion: Embracing Face Recognition Technology Responsibly
Embracing face recognition technology responsibly involves understanding its fundamentals, types, working principles, practical applications, and ethical considerations. Proper knowledge of these aspects ensures the balanced and ethical use of this powerful technology.
Exploring key elements such as detection, feature extraction, recognition techniques, applications in security and retail, and addressing common questions provides valuable insights. Recognizing the importance of privacy, fairness, and regulatory measures enhances overall understanding and responsible implementation.
By engaging with these elements, professionals, developers, and policymakers can confidently leverage face recognition algorithms while addressing ethical and societal concerns. Therefore, whether you are involved in developing, deploying, or regulating this technology, understanding face recognition algorithms offers practical and valuable insights. Embrace the opportunity to harness the power of face recognition technology responsibly, knowing you have the knowledge and resources to achieve ethical and effective solutions!