Facial expression recognition (FER) technology has emerged as a significant advancement within the fields of artificial intelligence and computer vision. By analyzing subtle nuances in facial expressions, FER systems can interpret human emotions and deliver a wide range of applications. Consequently, understanding the complexity, benefits, and ethical considerations of FER technology is critically important. Therefore, this comprehensive guide explores the underlying mechanisms, notable applications, and potential concerns associated with facial expression recognition. By delving into these aspects, you can grasp the profound impact and future prospects of this innovative technology.
Understanding the Mechanisms of Facial Expression Recognition
The functionality and precision of facial expression recognition systems are rooted in advanced computational techniques. Understanding these mechanisms provides insight into how FER systems interpret human emotions. Therefore, exploring the technology behind facial expression recognition is crucial.
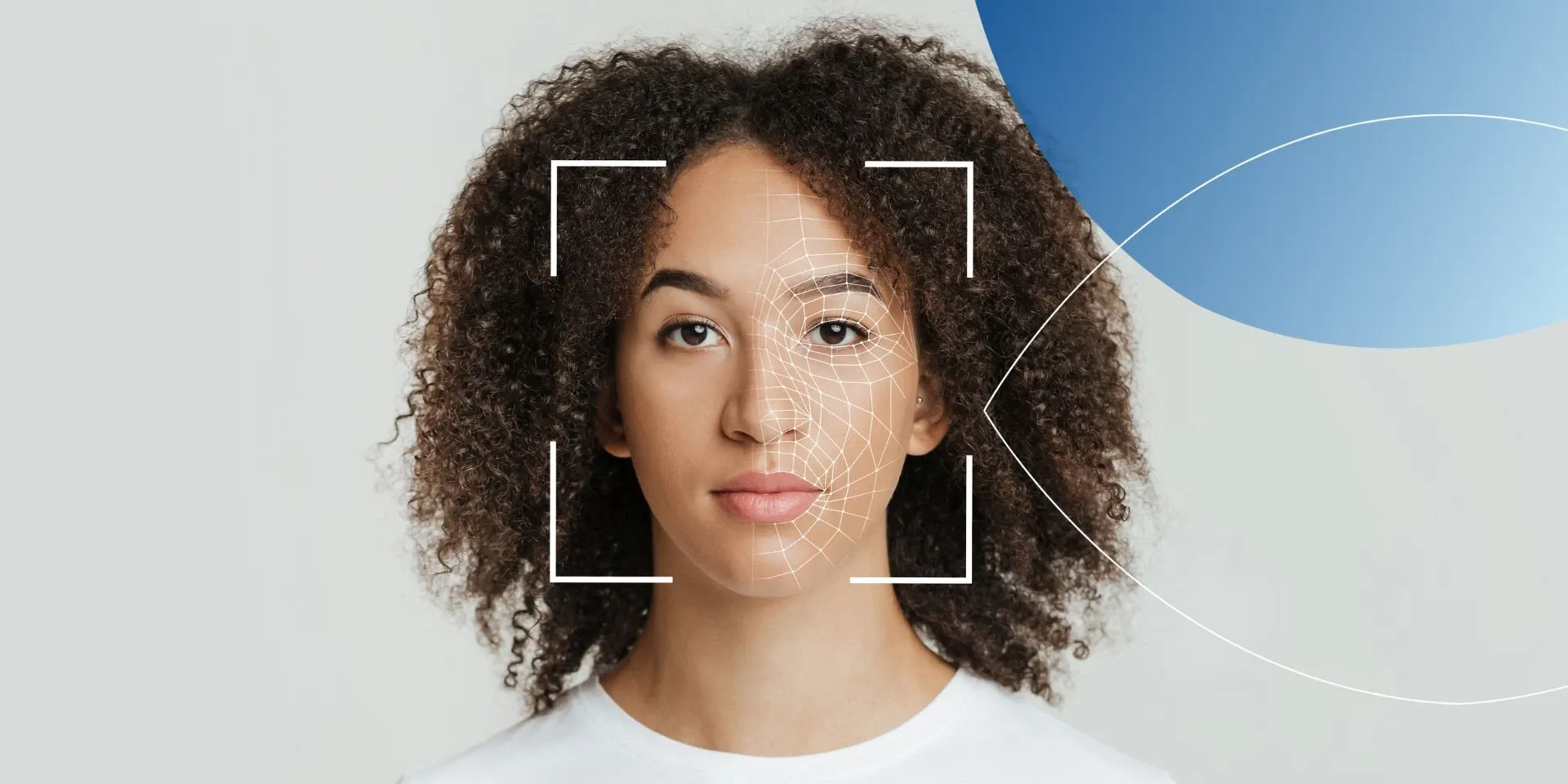

Computational Methods for Recognition
Facial expression recognition systems employ various computational methods to accurately analyze and interpret facial expressions. One of the core techniques utilized is machine learning, which enables systems to learn and improve from data over time. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a type of deep learning model, are particularly effective for image and pattern recognition tasks. These networks are trained on vast datasets of facial images, tagged with corresponding emotional labels. By processing these images through multiple layers of neurons, CNNs learn to detect specific features and patterns associated with different emotions. Additionally, approaches like facial landmark tracking and Optical Flow analysis capture dynamic changes in facial expressions. By understanding these computational methods, you can appreciate the sophistication behind FER systems. Therefore, recognizing the importance of machine learning and convolutional networks is crucial.
Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
Before a facial expression recognition system can analyze emotions, preprocessing and feature extraction stages are essential. Preprocessing steps often include image normalization, resizing, and noise reduction, to ensure consistent and high-quality input data. Feature extraction involves identifying key points or landmarks on the face, such as the eyes, eyebrows, nose, and mouth. These landmarks are tracked over time to assess how they move and change, providing insights into subtle facial expressions. Techniques like Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) and Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) assist in extracting these critical features. By understanding the preprocessing and feature extraction steps, you can appreciate how FER systems ensure accuracy and reliability. Therefore, recognizing the significance of these initial steps is essential.
Notable Applications of Facial Expression Recognition
Facial expression recognition technology offers numerous applications across multiple industries. Understanding these applications demonstrates the versatility and practical benefits of FER systems. Therefore, exploring the key use cases of facial expression recognition is essential.
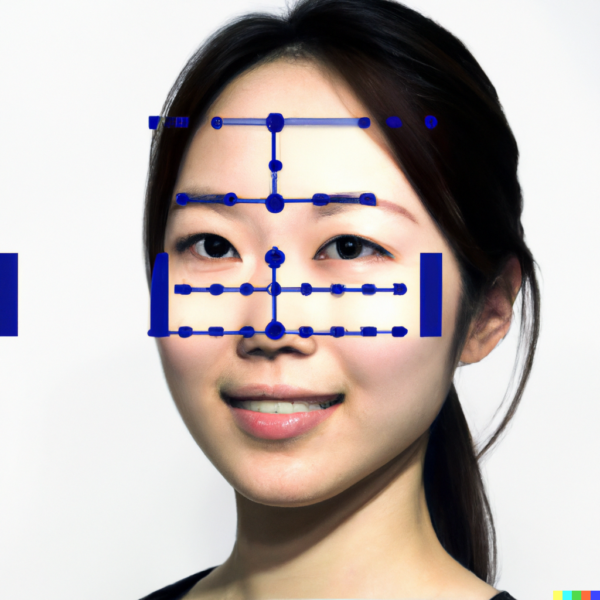
Enhancing Customer Experience in Retail
One notable application of facial expression recognition is in enhancing customer experience within the retail sector. By analyzing customers’ facial expressions as they shop, retailers can gain valuable insights into their emotions and preferences. For instance, FER systems can identify customer satisfaction, frustration, or curiosity as they interact with products or services. This real-time data enables retailers to make immediate adjustments, such as optimizing product displays or offering personalized assistance. Additionally, FER technology can be integrated with digital signage to display targeted advertisements based on a customer’s emotional response. By understanding the applications in retail, you can appreciate how FER technology enhances customer experiences. Therefore, recognizing the impact on customer insights and personalization is crucial.
Improving Mental Health Care
Facial expression recognition also plays a significant role in improving mental health care. Mental health professionals can use FER systems to monitor and assess patients’ emotional states accurately and objectively. For example, during therapy sessions, FER technology can detect subtle changes in facial expressions that might indicate stress, anxiety, or depression. This objective data complements traditional assessment methods, providing a more comprehensive understanding of a patient’s emotional wellbeing. Furthermore, FER systems can be incorporated into digital mental health applications, offering real-time feedback and support for individuals managing mental health conditions. By understanding the applications in mental health care, you can recognize the potential for improved patient assessments and interventions. Therefore, recognizing the value for mental health professionals and patients is essential.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Concerns
While facial expression recognition technology offers numerous benefits, it also raises significant ethical considerations and potential concerns. Understanding these issues ensures responsible and informed use of FER systems. Therefore, exploring the ethical implications and challenges is crucial.
Privacy and Consent
One of the most pressing ethical concerns associated with facial expression recognition is privacy. The collection and analysis of facial data without explicit consent can infringe on individuals’ rights to privacy and autonomy. Transparent policies and clear communication about the use of FER technology are necessary to ensure that individuals understand how their data will be used. Additionally, obtaining informed consent is essential, particularly in public spaces or clinical settings. By understanding the importance of privacy and consent, you can recognize the need for ethical guidelines and practices. Therefore, recognizing the significance of protecting personal privacy is crucial.
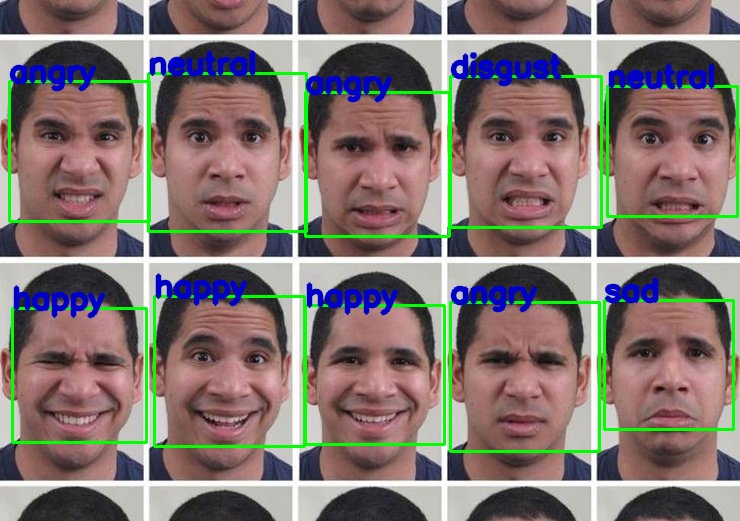

Bias and Discrimination
Another critical ethical issue is the potential for bias and discrimination in facial expression recognition systems. FER technology relies on training data to learn and interpret facial expressions accurately. However, if the training data lacks diversity or contains inherent biases, the system’s performance can be skewed, leading to inaccurate or discriminatory outcomes. For instance, FER systems trained on data primarily featuring specific demographic groups might perform poorly when analyzing individuals from underrepresented communities. Addressing these biases requires diverse and representative training datasets, along with ongoing evaluation and adjustment of algorithms. By understanding the potential for bias and discrimination, you can appreciate the importance of fairness and inclusivity in FER technology. Therefore, recognizing the need for unbiased and equitable systems is essential.
Addressing Common Questions About Facial Expression Recognition
Understanding common questions about facial expression recognition provides clarity and enhances your knowledge. Knowledge of these answers ensures better preparation and awareness of FER technology. Therefore, exploring common questions is essential.
How Accurate Is Facial Expression Recognition?
The accuracy of facial expression recognition systems depends on several factors, including the quality of training data, the complexity of the algorithms, and the conditions under which the technology is used. High-quality datasets and advanced computational methods like CNNs typically yield more accurate results. However, factors such as lighting, camera angles, and facial occlusions can impact the system’s performance. Continuous refinement and validation of FER algorithms are necessary to maintain and improve accuracy. By understanding the factors influencing accuracy, you can appreciate the importance of quality data and rigorous testing. Therefore, recognizing the need for ongoing improvement is crucial.
Can Facial Expression Recognition Be Used in Real-Time Applications?
Yes, facial expression recognition technology can be used in real-time applications. Advances in computational power and algorithm efficiency enable FER systems to process facial data and analyze emotions almost instantaneously. Real-time FER applications include customer service kiosks, interactive marketing displays, and mental health monitoring tools. These applications offer immediate insights and feedback, enhancing user experiences and facilitating timely interventions. By understanding the potential for real-time applications, you can recognize the versatility and practicality of FER technology. Therefore, recognizing the value of real-time insights is essential.

Addressing Common Misconceptions About Facial Expression Recognition
Addressing common misconceptions about facial expression recognition provides accurate information and dispels unwarranted concerns. Clearing up misunderstandings ensures an informed perspective. Therefore, exploring common misconceptions is important.
Misconception: Facial Expression Recognition Invasion of Privacy
A common misconception is that facial expression recognition technology inherently violates privacy. While FER technology involves the collection of facial data, responsible implementation and clear consent policies can mitigate privacy concerns. By ensuring that individuals are informed about the use of FER and given the option to opt-in or opt-out, privacy can be respected. Organizations should establish transparent data practices and prioritize data security to maintain trust. By understanding the nuanced approach to privacy, you can appreciate the responsible use of FER technology. Therefore, dispelling this misconception highlights the importance of ethical implementation.
Misconception: Facial Expression Recognition Always Accurate
Another misconception is that facial expression recognition technology is always accurate and infallible. In reality, FER systems can experience limitations and inaccuracies, influenced by factors such as environmental conditions, diverse facial features, and varying emotional expressions. Continuous improvement and validation are necessary to enhance accuracy and reliability. By understanding the limitations of FER technology, you can appreciate the need for ongoing refinement and realistic expectations. Therefore, dispelling this myth emphasizes the importance of acknowledging technology boundaries.

Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of Facial Expression Recognition
Facial expression recognition technology represents a significant advancement in understanding and interpreting human emotions. Proper preparation, including recognizing the underlying mechanisms and notable applications, sets the foundation for informed awareness.
Exploring critical aspects such as privacy concerns, ethical considerations, and addressing common questions ensures a comprehensive understanding. Recognizing the importance of addressing misconceptions enhances your overall knowledge and appreciation for FER technology.
By engaging with these elements, you can gain deeper insights into the significance, applications, and ethical implications of facial expression recognition. Therefore, whether you are a technology enthusiast, industry professional, or ethical advocate, understanding the essential considerations and future prospects of FER technology offers practical and thought-provoking insights. Embrace the opportunity to explore and comprehend facial expression recognition, knowing you have the knowledge and resources to appreciate its complex and transformative impact!


